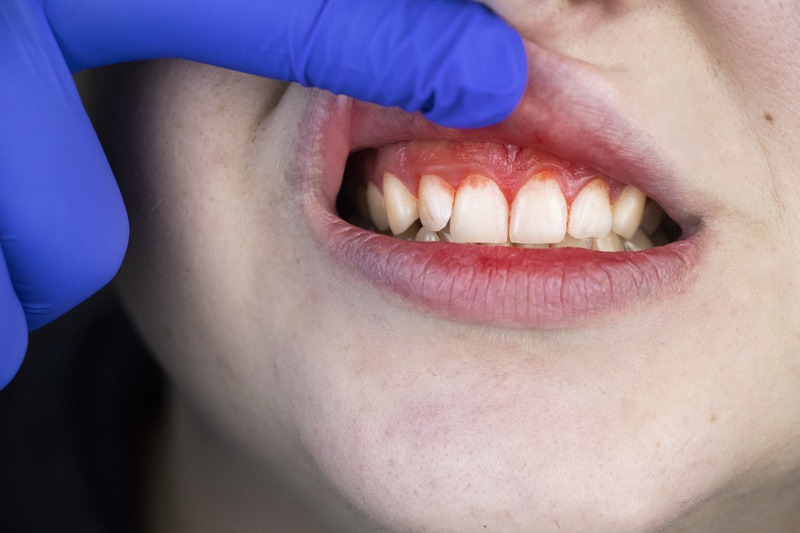
Periodontal diseases, encompassing conditions such as gingivitis and periodontitis, constitute a significant public health concern due to their prevalence and potential to cause severe oral health problems. These diseases primarily affect the gums and the supportive structures of the teeth, leading to symptoms ranging from mild gum inflammation to severe damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth.
If left untreated, periodontal diseases can lead to tooth loss and have been linked to other serious health issues such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Types of Periodontal Diseases
1. Periodontitis
-
If gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to periodontitis, a more severe periodontal disease that destroys the gums, ligaments, and alveolar bone.
-
Symptoms include receding gums, the formation of deep pockets between the teeth and gums, loose or shifting teeth, persistent bad breath, and even tooth loss.
-
Periodontitis requires more intensive treatment, such as scaling and root planing, and in severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to restore oral health.
To prevent such severe outcomes, it’s crucial to maintain your oral health with periodontal maintenance, which can help manage symptoms and prevent the progression of gum disease.
2. Gingivitis
-
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease and is characterized by inflammation of the gums. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth.
-
Symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen gums that may bleed easily during brushing or flossing.
-
This condition is usually painless and reversible with good oral hygiene and regular professional dental cleanings.
3. Advanced Periodontitis
-
In advanced periodontics services, the fibers and bone supporting the teeth are severely damaged, which can cause teeth to become loose or fall out.
-
This stage requires aggressive treatment, possibly surgery, and regenerative procedures to repair the supporting structures.
How Can Periodontal Diseases Be Prevented?
Preventing periodontal diseases involves adopting and maintaining good oral hygiene practices, regular dental visits, and lifestyle choices that support gum health. Here are essential preventive measures:
1. Regular Brushing
Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent gum damage, and ensure you brush for at least two minutes, covering all tooth surfaces and along the gum line.
2. Daily Flossing
Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between the teeth and under the gum line where a toothbrush cannot reach. This helps prevent plaque buildup, which can lead to gum disease.
3. Professional Dental Cleanings
Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings with your dentist every six months. Professional cleanings remove tartar (hardened plaque) that cannot be removed by brushing and flossing alone, and they allow for early detection of any signs of gum disease. Furthermore, bone grafting can support dental implants, ensuring a solid foundation for those who require such treatments.
4. Healthy Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and calcium, supports gum health. Limiting the intake of sugary and starchy foods can reduce the risk of plaque formation. Instead, choose fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and dairy products.
5. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease as it impairs blood flow to the gums and hinders the healing process. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and improve overall oral health.
6. Use Mouthwash
Use an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash to help reduce plaque, fight bacteria, and prevent gum inflammation. Mouthwashes can reach areas that brushing and flossing might miss, providing additional protection.
7. Proper Dental Care Tools
Use dental care tools like interdental brushes, water flossers, or soft picks to clean between teeth effectively, especially if you have braces, bridges, or other dental appliances that make traditional flossing challenging.
8. Monitor Your Gum Health
Be vigilant about any changes in your gums, such as redness, swelling, bleeding, or persistent bad breath. Early detection and treatment of gum problems can prevent the progression to more serious periodontal diseases. If you notice any signs of gum disease, seek professional dental care promptly.
9. Education and Awareness
Educate yourself about the signs and symptoms of periodontal diseases and the importance of oral health. Understanding the risks and what to look for can help you take proactive steps to prevent gum disease.
10. Hydration
Staying hydrated helps maintain the flow of saliva, which plays a crucial role in washing away food particles and bacteria and in neutralizing acids in the mouth that cause tooth decay and gum disease.
Wrapping Up
Periodontal diseases are severe conditions that can significantly impact oral and overall health if left untreated. You can significantly reduce your risk of developing periodontal diseases by maintaining diligent oral hygiene practices, having regular dental check-ups, adopting a healthy diet, and making informed lifestyle choices. Early detection and treatment are critical for managing these conditions effectively and ensuring your gums and teeth stay healthy.